According to medical statistics, acute back pain is the second most common cause of disability. At least 80% of people have suffered from them at least once. They can occur sporadically or be observed with worsening spinal diseases. In any case, acute and chronic back pain require competent treatment and targeted action on the causes of their occurrence.
Acute back pain: caused by
Acute pain lasts for less than 6 weeks. For most, it will pass within 2 weeks. Although it is initially impossible to predict how long it will last. Nevertheless, in almost half of the cases, similar or more severe seizures recur later and become chronic pain.
Acute pain can be of varying intensity, dull, burning, and so on. Sometimes it can radiate to the arms, legs, and buttocks. So-called back pain often occurs as a result of hypothermia, excessive physical exertion, and sprains. Several days may elapse between the effect of the traumatic factor and the immediate onset of the pain syndrome and manifest as a result of mild physical exertion such as bending.
There may be consequences of back injury or the first appearance of spinal diseases, including:
- osteochondrosis;
- intervertebral hernia;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- spinal stenosis, etc.
Increase the likelihood of back problems:
- common stress;
- regular increased physical activity;
- overweight;
- is a common and long-lasting job.
In addition to severe back pain, headaches, burning sensations in the legs, and dizziness may also occur. All of these symptoms should be reported to the doctor at the meeting.
Regardless of which anatomical structure is damaged first, this involves a series of consecutive changes that increase the discomfort. Initially, inflammatory factors are formed in the lesion, causing swelling and irritating nerve fibers. In response, muscle cramps often occur, which further aggravates the situation and causes circulatory disorders in the affected area. This leads to a decrease in the amount of nutrients and oxygen that the lesion focuses on, as well as a retention of metabolic products.
Treating Acute Back Pain
Lie on your back on a hard surface to relieve pain. This allows the back muscles to relax and relieves spinal stress. To enhance the effect, orthopedic pillows can be placed under the knee and under the head, but it is important to avoid sagging of the lower back. In case of severe pain, short-term administration of the NSAID group is allowed. In the future, you should definitely contact a neurologist or spine surgeon to determine the cause of your pain syndrome.
You should see a doctor as soon as possible if there is no improvement within a week, an attack or irradiation of the foot or knee pain, urinary incontinence, and defecation. To diagnose pre-existing conditions, patients are shown:
- MRI;
- CT;
- X-ray;
- biochemical blood test;
- UAC.
Based on the results of the research and the characteristics of the symptoms, the doctor makes a diagnosis and develops treatment tactics. In the case of acute pain, which deprives a person of the ability to work, they may be offered to perform a spinal block, which alleviates the pain syndrome in a matter of minutes.
Once the discomfort is over, it is important not to linger in bed. Moderate physical activity, supplemented by special exercises in medical gymnastics, is the best prevention for the recurrence of such attacks in the future.
If you go to the hospital, you will definitely get high quality treatment for your pain syndrome and its causes. Professionals will be able to develop the most effective treatment tactics and quickly relieve pain with a well-made, affordable blockade.
Chronic back pain: causes
People suffer from chronic back pain just as often. They can get worse and become an attack of acute pain that completely shuts a person off their normal rhythm. The most common consequences are:
- A sedentary lifestyle that leads to a weakening of the muscular corset. This provokes an increase in spinal load and compression of the vertebrae. The result is osteochondrosis, a protrusion of the intervertebral discs and herniated intervertebral discs, spondyloarthrosis.
- Postural disorders. Long-term preservation of any position of the body in which the natural curves of the spine are interrupted provokes its curvature and the development of scoliosis or kyphosis. This involves degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs, redistribution of muscle load, and stinging of nerve roots.
- Weakening of the abdominal muscles. Because they act as supports for the internal organs and partially relieve the spine, their weakness increases the load on the lower back, which increases lordosis and causes chronic pain. In addition to a sedentary lifestyle, weakening of the abdominal muscles can be the result of pregnancy or obesity.
- Age changes. Over the years, intervertebral discs gradually dry out, causing a decrease in their elasticity, strength, and size. The annular fibrosis surrounding the gelatinous core dries out and becomes more brittle. The loads cause cracks to form in it, leading to bulges and hernias. The resulting protrusion can pinch closely lying blood vessels, nerve roots, spinal cord, which provokes the appearance of pain.
The diseases of chronic back pain are as follows:
- osteochondrosis;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- osteoporosis;
- intervertebral hernia;
- facet syndrome;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- spondylolisthesis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- oncological diseases and others.
A common cause of chronic pain is deterioration of the facet joints. The cartilage in them tends to thin out by overloading the spine. As a result, the shock-absorbing functions that cause friction of bone fragments and the development of inflammation are eliminated during movement.
Treating Back Pain
Treatment tactics are developed based on the abnormalities discovered during diagnostic tests. Conservative therapy is initially prescribed for the detection of spinal diseases, including:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- exercise.
Conservative therapy
A holistic, individualized approach is important in treating back pain. Depending on the cause, patients are prescribed a number of medications, especially:
- NSAIDs - medicines in this group have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, but their long-term use negatively affects the condition of the digestive system;
- corticosteroids - drugs with a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, prescribed in moderate to severe cases;
- muscle relaxants - help eliminate increased muscle tone and cramps;
- antidepressants - help eliminate psychological discomfort, which often reduces the effectiveness of conservative therapy;
- topical agents - ointments or gels containing anti-inflammatory, warming or cooling components can help reduce the severity of pain and have virtually no side effects;
- Chondroprotectors - formulations containing glucosamine and chondroitin have a beneficial effect on the condition of cartilage tissue, increase its elasticity and help restore normal thickness.
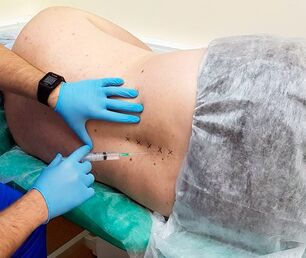
In mild cases, oral medication is sufficient. But in more complex situations, intraarticular injections may be prescribed to patients. In case of severe pain, blockages should be performed once or throughout the course, which can include up to 10 procedures.
In order to increase the effectiveness of drug therapy, patients are prescribed massage and physiotherapy. The right effect on the back muscles helps to activate blood and lymph flow, improve metabolic processes and eliminate muscle cramps. Manual therapy is very effective in spinal deformities, especially in 1-2 degree scoliosis. Regular exercises help restore the normal position of the spine and relieve pressure on the internal organs.
As part of physiotherapy, patients receive sessions:
- UHF;
- magnetic therapy;
- Bernard currents;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- UFO;
- balneological treatment.
If the condition cannot be improved within six months or there is a risk of complications, patients may be offered surgical treatment for pre-existing conditions.
Surgical treatment
Modern methods of surgery are characterized by a high level of efficiency and safety. They allow for the rapid elimination of the pathological cause of the development of pain syndrome and often do not require a hospital stay. But most minimally invasive and microsurgical methods can only be used if patients consult a spinal surgeon early in the course of the disease.
The indications for surgical treatment are as follows:
- progressive herniated intervertebral discs;
- spinal stenosis;
- separated hernia; spine fractures;
- 3-4. grade scoliosis;
- severe forms of spondyloarthrosis;
- compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots;
- hemangiomas of the vertebral bodies;
- instability of certain segments of the spine;
- cauda equina syndrome.
The surgeon determines the type of surgery based on the severity of the patient's condition. With the same diagnosis, surgical treatment can be performed in different ways, different in terms of the degree of invasiveness, effectiveness, duration and cost of rehabilitation.
Recently, minimally invasive methods of surgical treatment have become very popular. They are used to treat intervertebral protrusions, intervertebral disc hernias, hemangiomas, and many other diseases. Minimally invasive surgery takes up to an hour, and upon completion, the patient can walk almost immediately and leave the clinic the same or the next day.
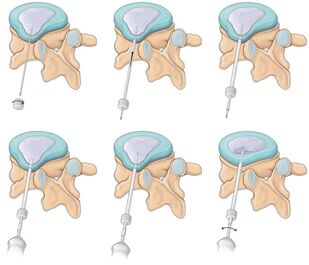
The great advantages of the method are the good cosmetic effect (in most cases all the necessary surgical instruments are inserted through the punctures of the soft tissues), the easy rehabilitation and the affordable price. For intervertebral hernias, only cold plasma nucleoplasty or hydroplasty (hydrodiscectomy) can be considered a more promising method.
In situations where microsurgical techniques cannot be used, surgeons perform open procedures. In doing so, it is possible to completely remove abnormally altered formations, compensate for severe deformations of the spine, replace irreparable structures with implants, and achieve normal spinal function by fixing metal titanium structures.
Modern spine surgery can solve almost any back problem. The latest methods of surgical treatment of spinal diseases are available in many institutions. A team of doctors with different profiles will help you get rid of acute or excruciating chronic back pain as soon as possible.
Preventing back pain
After the seizure is over and the pain is boring, it is recommended to avoid another episode:
- Do not lift objects that are too heavy;
- do not bend;
- keep walking;
- gives up hard physical work; Take regular breaks to warm up while sitting
- .



































